Difference between Microprocessor and Microcontroller – Computer Science for dummies.

The terms microprocessor and microcontroller have always been a hell of confusion for first semester computer science students. Those two share many common features and at the same time they have significant differences. Visually if an untrained person takes a look at any microcontroller or microprocessor, he would hardly detect any difference between those two products.
However those two are almost entirely different in many practical aspects. Those differences present themselves in terms of application, production cost, processing power as well as consuming power and inclusive or rather exclusive peripheral functions.
The classic example of a microprocessor application is a laptop, that kind of maschine you use to watch your favorite YouTuber, do Microsoft Excel or any kind of possible digital work. A microprocessor is basically just a CPU (Central Processing Unit) without any predifined task. A system designer has to equip them externally with USB-Port, keyboard, mouse, memory, sensors, etc. to make them functional. The most popular microprocessor suppliers are AMD, Intel and Apple.
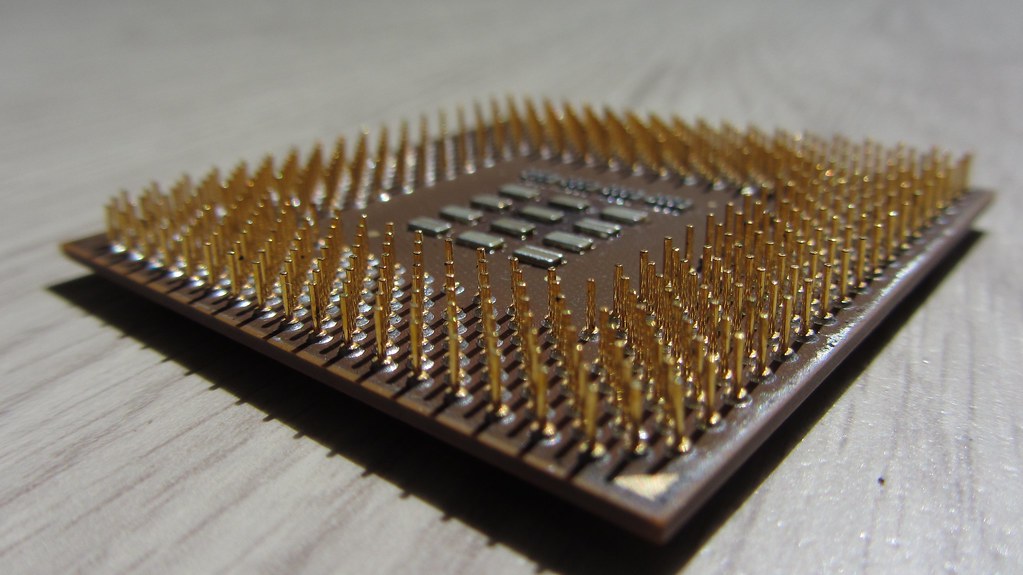
Meanwhile in a case of microcontrollers, they are mostly used for a very specific task in order to reduce the cost and consuming power. Example for microcontroller applications are refrigerator, microwave, car etc. These devices are very simple and limited comparing to a modern laptop, I mean a microwave should only be able to cook food and not simulate thermodynamics. Because of its limited functions a microcontroller has all of its memory elements, input/output interface integrated along with the CPU inside a single chip. This in turn reduces the size and the cost. Depending on the definition a microcontroller could almost be termed as a mini computer or a computer on a single chip. Famous producers of microcontrollers are Texas Intruments, Intel, Raspberry Pi, Arduino.

Moreover microprocessors operate at much higher speed than microcontrollers. Whereas the microcontrollers operate from a few MHz to 50 MHz, today’s microprocessor operate above 1 GHz to the 4 GHz for the high-end processors. The sames applies to term of RAM (Ramdom-Access-Memory and ROM (Read Only Memory).
In conclusion, comparing microcontroller and microprocessor in terms of cost is not justified. Undoubtedly a microcontroller is far cheaper than a microprocessor. However microcontroller cannot be used in place of microprocessor and using a microprocessor is not advised in place of a microcontroller as it makes the application inefficiently.