On Time and Space Complexity
#datastructures #algorithmns #devstudy #BigONotation #timecomplexity #spacecomplexity
Time Complexity: Time taken to run as a function of the length of the input
- number of operations it takes to complete for length Input
- find the WORST CASE scenario > drop the non-dominant terms
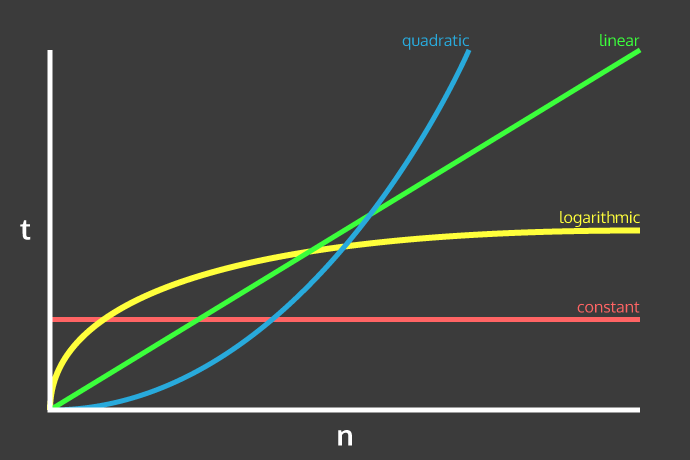
Not the most useful chart but that pastel-tone charcoal = yes
Better chart but less aesthetic:
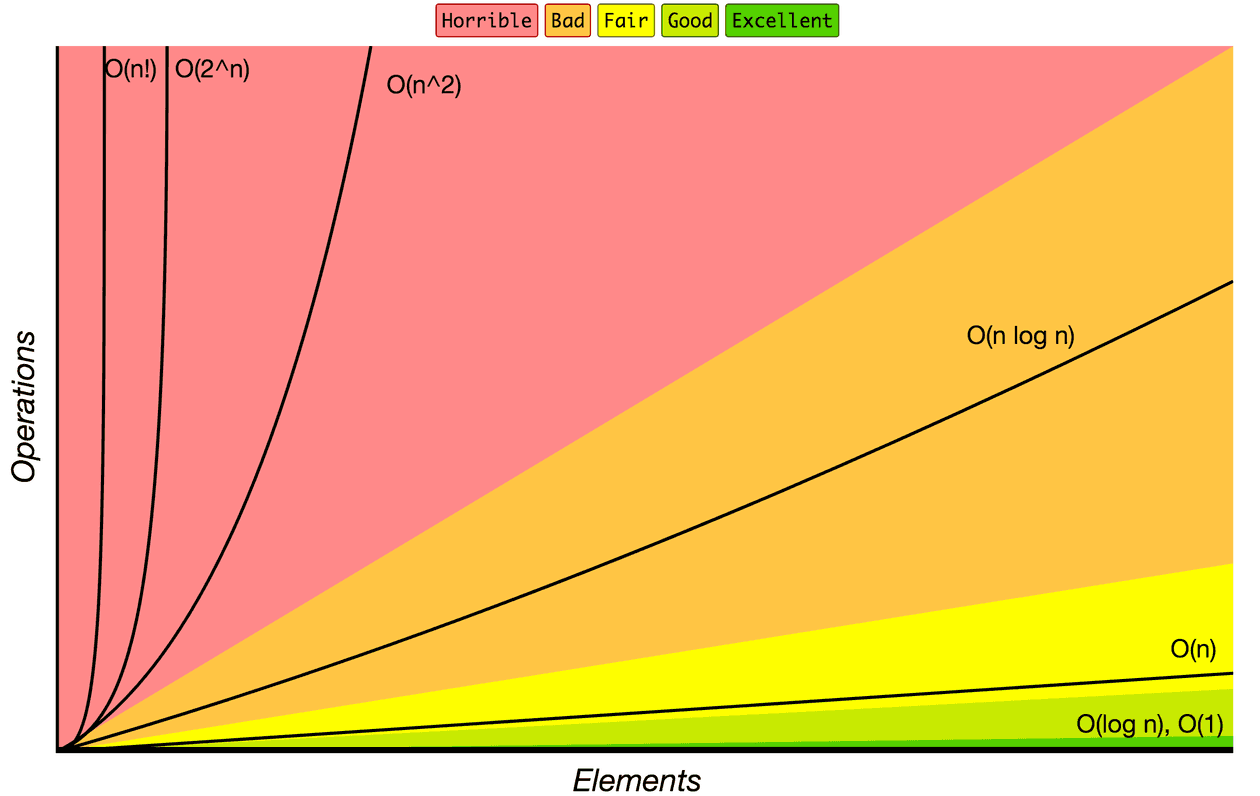
From Fastest to Slowest:
O(1) time: One Operation
- takes a constant amount of time even with more input
- ex: mathematical calculation of sum:
s = n(a+1)/2as opposed iterative calculation which isO(n)linear bc for every additional input value, the rate of growth re: time scales proportionally.
Examples
- accessing Array Index
- Inserting a node in Linked List
- Pushing and Popping on Stack
- Insertion and Removal from Queue
- Finding out the parent or left/right child of a node in a tree stored in Array
- Jumping to Next/Previous element in Doubly Linked List
O(log n) time: Recursion?
Examples
- Binary Search
- Finding largest/smallest number in a binary search tree
- Certain Divide and Conquer Algorithms based on Linear functionality
- Calculating Fibonacci Numbers – Best Method premise = NOT using the complete data, and reducing the problem size with every iteration
O(n) time: Linear, i.e. Brute Force, Noob ones that I write bc my brain is stuck on iteration
Examples
- Traversing an array
- Traversing a linked list
- Linear Search
- Deletion of a specific element in a Linked List (Not sorted)
- Comparing two strings
- Checking for Palindrome
- Counting/Bucket Sort and here too you can find a million more such examples....
O(n*log n) time: linear time complexity multiplied by log n
- factor of
log nis introduced by bringing into consideration Divide and Conquer. - some of the most optimized and frequently used
Examples
- Merge Sort (recursive)
- Heap Sort
- Quick Sort
- Certain Divide and Conquer Algorithms based on optimizing
O(n^2)algorithms
O(n^2) time: Quadratic.
- nested loops bc each loop is performing
niterations son*n - less efficient algorithms if their
O(n*logn)counterparts are present?? - general application may be Brute Force here
Examples
- Bubble Sort :'(
- Insertion Sort
- Selection Sort
- Traversing a simple 2D array
Space Complexity: The space an algo needs to run
- sorting algorithmns need at least
O(n)space to save the list of lengthnthat they have to sort but can often workin placemeaning that it needs no additional space - number representation can be saved in either (1) binary (or any other base equal or less than 2) so this needs
O(log n)space bcn = 2^logn; or (2) as a sum ofnso you needO(n)space bc you need to save eachn
O(1) space: In-place
- a function that counts the elements of an array: don't need to allocate or copy new data even if the array is large, the counter is the same var
O(log n) space:
Examples
- Binary Search
- Finding largest/smallest number in a binary search tree
- Certain Divide and Conquer Algorithms based on Linear functionality
- Calculating Fibonacci Numbers – Best Method premise = NOT using the complete data, and reducing the problem size with every iteration
O(n) space:
- everytime we make a new function call = new stack frame
- recursion: if
n= 100, thenO(n)